CRISPR Gene Editing: Balancing Cure and Ethics
- admin
- 0
- Posted on
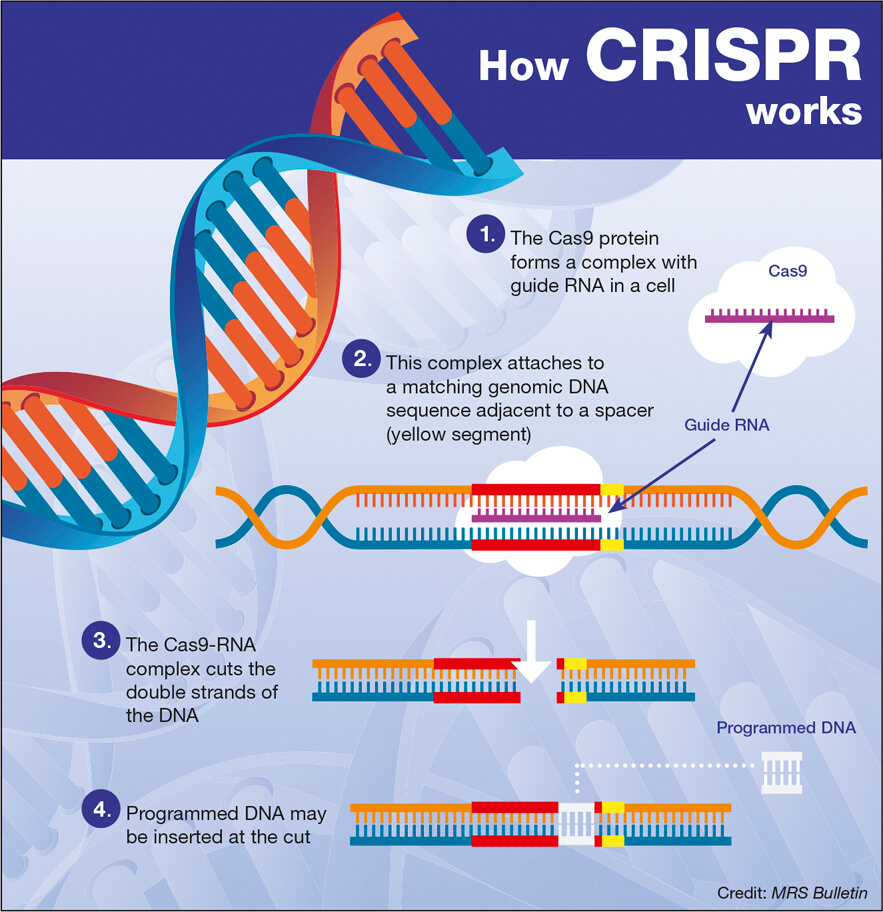
CRISPR gene editing has revolutionized the field of genetics, offering unprecedented opportunities to modify DNA with precision. This groundbreaking technology enables scientists to target specific genes that underlie various health conditions, such as sickle cell disease, providing hope for curing ailments once thought incurable. However, as the potential of CRISPR technology unfolds, it also raises significant ethical debates concerning genetic modification and health equity. The complexities surrounding gene editing ethics come into sharp focus when considering who decides which genes are modified and the implications of such decisions on future generations. As we stand on the brink of a new era in medicine, the promise of CRISPR gene editing calls for a critical examination of its benefits and the moral responsibilities it demands.
Gene editing, often referred to as genetic modification, represents a transformative shift in our ability to manipulate the very code of life. Utilizing advanced techniques such as CRISPR technology, researchers can make targeted changes to specific genetic sequences, opening the door to potential cures for conditions like sickle cell anemia. Nevertheless, the discussion surrounding gene modification is fraught with ethical questions that challenge our understanding of human rights and societal values, particularly regarding health equity and access to these innovative treatments. As we delve deeper into this sensitive subject, it becomes imperative to navigate the fine line between therapeutic advancement and the potential repercussions of altering human genetics. Ultimately, the implications of these scientific breakthroughs demand a careful and informed dialogue among scientists, ethicists, and policymakers.
The Ethical Considerations of CRISPR Gene Editing
The advent of CRISPR gene editing has sparked heated discussions about its ethical implications. Central to these conversations is the question of whether we should intervene in the human genome to eliminate diseases like sickle cell disease. While many see this as a revolutionary opportunity to improve health outcomes, others worry that it could lead to a slippery slope of genetic modification. The debate continues on whether altering genes for diseases that allow individuals to lead fulfilling lives, such as Down syndrome, crosses an ethical line. These dilemmas highlight the need for a stringent ethical framework guiding the use of gene editing technologies.
Moreover, who decides the parameters of acceptable gene modifications? The voices of bioethicists, geneticists, and affected families must contribute to these discussions, ensuring that diverse perspectives shape policies around this powerful technology. As we navigate these uncharted waters, it is crucial to remember that while CRISPR brings hope, it also carries the weight of moral responsibility and the potential for unintended consequences.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the ethical implications of CRISPR gene editing in treating diseases like sickle cell disease?
The ethical implications of CRISPR gene editing in treating conditions like sickle cell disease revolve around crucial questions of consent, accessibility, and the long-term effects of genetic modification. Needing to weigh the potential benefits, such as curing debilitating diseases, against the risks of unintended consequences and the moral responsibility of altering human genetics remains a central debate.
How does CRISPR technology potentially impact health equity for diseases like sickle cell disease?
CRISPR technology’s impact on health equity is significant, particularly for diseases like sickle cell disease, which disproportionately affects marginalized communities. The high cost of CRISPR-based treatments raises concerns regarding who can access these therapies, highlighting disparities in healthcare and the need for policies that ensure fair distribution and accessibility.
Can CRISPR gene editing be used ethically for genetic modifications beyond curing diseases?
The ethical use of CRISPR gene editing for genetic modifications beyond curing diseases is a contentious topic. While some argue it could help eliminate certain conditions, there are concerns about ‘designer babies’ and the societal implications of selecting for specific traits. The debate includes questions of parental rights and the potential for exacerbating social inequality.
What are the potential risks of using CRISPR gene editing on germline cells?
Using CRISPR gene editing on germline cells presents several risks, including unforeseen genetic changes that could lead to health problems in future generations. The long-term effects of such modifications are still largely unknown, making this area a significant focus of ethical discourse in genetic modification.
What role does oversight play in the ethical application of CRISPR technology?
Oversight is critical in ensuring the ethical application of CRISPR technology. With concerns about unregulated research and applications occurring in countries with lax laws, effective monitoring and legislative frameworks are necessary to prevent misuse and to safeguard against harmful modifications in human genetics.
How does CRISPR gene editing address the challenges of diseases like sickle cell disease?
CRISPR gene editing addresses the challenges of sickle cell disease by targeting and repairing the genetic mutations responsible for the condition. This innovative approach has the potential to offer permanent solutions, significantly improving the quality of life for affected individuals while opening up discussions on the ethics of genetic modification.
Is there a risk of widening health disparities through CRISPR gene editing technologies?
Yes, there is a significant risk of widening health disparities through CRISPR gene editing technologies. As access to these advanced treatments may be limited by socioeconomic status, those who can afford them may benefit disproportionately, thus exacerbating existing health inequities in society.
What questions should be considered regarding gene editing ethics in the context of CRISPR?
Key questions regarding gene editing ethics in the context of CRISPR include the justification for editing genes linked to disabilities, who determines the ethical limits of gene modification, and how to ensure equitable access to gene therapies to prevent deepening social divides.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| CRISPR Gene Editing Capabilities | CRISPR can edit somatic and germline genes, potentially curing genetic diseases such as sickle cell anemia. |
| Ethical Considerations | Questions arise regarding the appropriateness of gene editing for conditions like Down syndrome and the implications for parental choice. |
| Cost and Accessibility | The cure for sickle cell anemia costs approximately $2.2 million, raising concerns about who will pay and equity in access. |
| Societal Implications | Gene editing could exacerbate existing inequalities, and society must consider the health justice implications of such innovations. |
| Oversight and Regulation | Concerns exist regarding the lack of monitoring in countries with looser regulations around gene editing. |
| Unintended Consequences | Editing genes can result in unforeseen effects due to the complex interactions of genes over time. |
Summary
CRISPR gene editing represents a revolutionary advancement in medical science, offering the potential to cure genetic diseases while simultaneously raising significant ethical questions. The dialogue surrounding its capabilities highlights a delicate balance between the promise of healing and the risks of ethical dilemmas and societal inequities. It is crucial to address these issues thoughtfully to ensure that the progress in gene editing brings equitable health solutions for all.