U.S. Maternal Mortality: A Growing Concern for Mothers
- admin
- 0
- Posted on
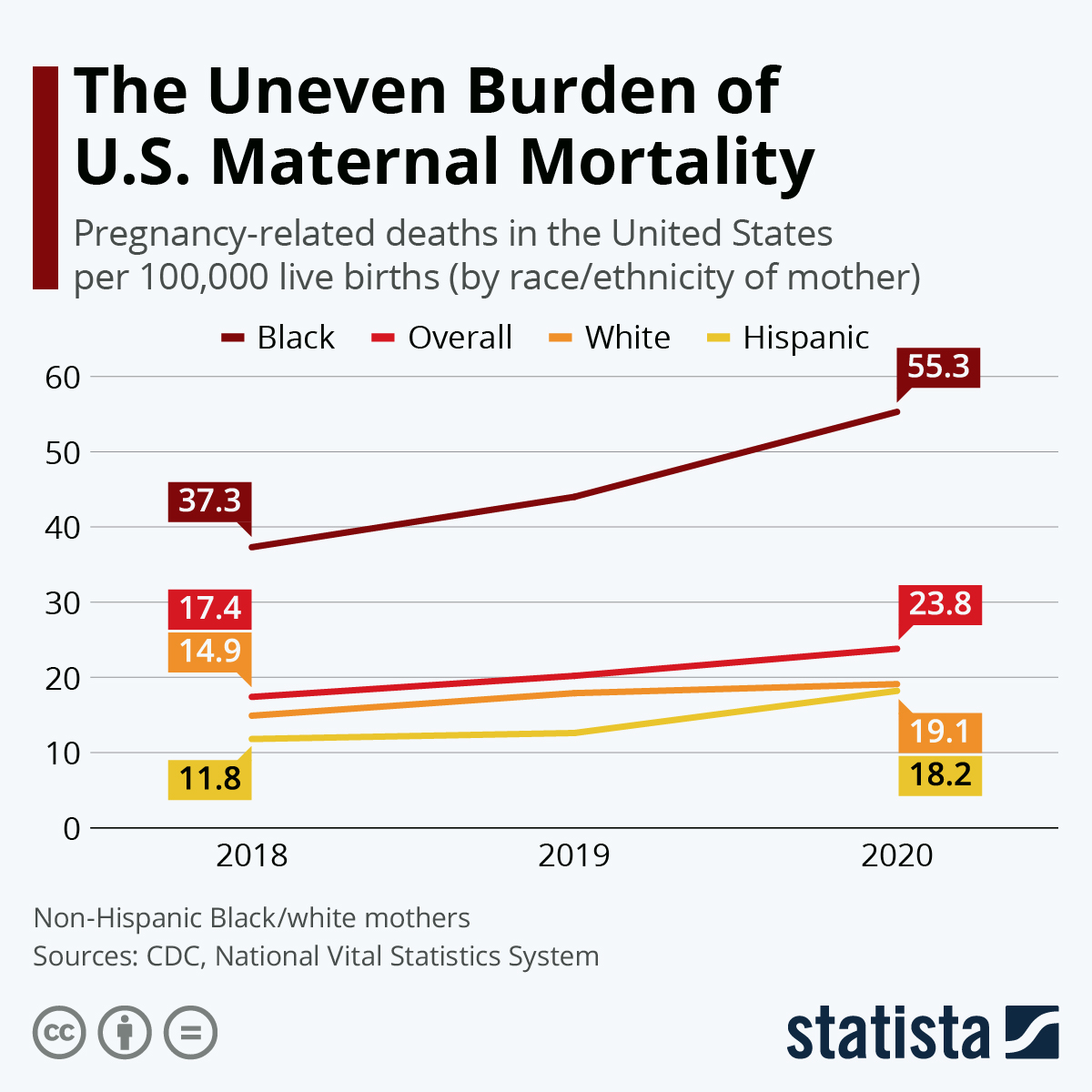
U.S. maternal mortality continues to rise, highlighting a concerning trend among pregnancy-related deaths in the nation. Despite being a high-income country, the United States has one of the highest maternal mortality rates, with more than 80 percent of these deaths being preventable. Recent maternal health statistics reveal stark disparities influenced by race and state, illustrating that American Indian and Alaska Native women face significantly higher mortality rates. Experts indicate that cardiovascular disease during pregnancy is a leading cause of these fatalities, necessitating enhanced postpartum care. Addressing these complex issues requires a multifaceted approach to tackle the racial disparities in maternal mortality and improve overall women’s health outcomes.
Maternal health challenges in the U.S. reflect a broader public health crisis, often described in terms such as pregnancy-related mortality or maternal health disparities. The rising number of pregnancy-associated deaths signals critical gaps in healthcare services, particularly in prenatal and postpartum care. These issues disproportionately affect marginalized communities, underscoring the urgency of addressing systemic healthcare inequities. As researchers uncover distressing trends, such as increased rates of cardiovascular complications in expectant mothers, it becomes clear that addressing these concerns requires immediate attention. Comprehensive strategies must be developed to improve health outcomes and ensure that all women have access to the quality care they deserve throughout their pregnancy journey.
Understanding U.S. Maternal Mortality Rates
The United States has consistently struggled with high maternal mortality rates, especially in comparison to other high-income countries. Between 2018 and 2022, the rates continued to rise, indicating an urgent need for reform in maternal healthcare. A staggering 80% of pregnancy-related deaths are deemed preventable, suggesting that with the right interventions, many lives could be saved. Factors contributing to these alarming statistics include a fragmented healthcare system, systemic inequities, and demographic disparities that disproportionately impact women of color. In particular, American Indian and Alaska Native women have a mortality rate nearly four times that of white women, highlighting the critical importance of addressing racial disparities in maternal health resources and policies.
One significant factor driving the rising maternal mortality rate in the U.S. is the increase in chronic health conditions such as cardiovascular disease among pregnant women. This transition in leading causes of pregnancy-related deaths from hemorrhage to cardiovascular-related issues indicates that more women are entering pregnancy with preexisting health challenges. Furthermore, the lack of comprehensive and inclusive postpartum care worsens these problems. Many women are left without adequate support or monitoring after childbirth, leading to late maternal deaths that often go unrecognized in traditional maternal mortality statistics. Addressing these issues require a commitment to enhancing both prenatal and postpartum care, ensuring that all women, regardless of race or socioeconomic status, receive the care they need throughout their reproductive years.
The Impact of Cardiovascular Disease During Pregnancy
Cardiovascular disease has emerged as a leading cause of maternal mortality, accounting for over 20% of pregnancy-related deaths in recent studies. Factors such as hypertension, pre-eclampsia, and other heart conditions are becoming increasingly common among pregnant individuals, and they pose significant risks not only during pregnancy but also afterward. This shift highlights the necessity of monitoring cardiovascular health in pre-pregnant and pregnant women to mitigate these risks. Because cardiovascular issues can arise before and during pregnancy, enhancing access to healthcare for all women can help identify risk factors early, thereby allowing for better management and prevention strategies.
The rise in maternal deaths related to cardiovascular events also emphasizes the importance of education and awareness initiatives aimed at both healthcare providers and patients. Training healthcare professionals to recognize the signs of cardiovascular complications during pregnancy is crucial. Additionally, community outreach programs designed to raise awareness about the risks of heart disease in pregnant women can empower patients to seek timely medical advice. By prioritizing cardiovascular health and integrating it into maternal care protocols, we can potentially reduce the risk of pregnancy-related fatalities and improve overall maternal health outcomes.
Racial Disparities in Maternal Mortality
The stark differences in maternal mortality rates experienced by racial and ethnic groups in the U.S. call for comprehensive changes in healthcare policies and practices. For instance, the data shows that Black and Native American women face significantly higher rates of pregnancy-related deaths compared to their white counterparts. These disparities are often attributed to a combination of socio-economic factors, systemic racism, and limited access to quality healthcare services. Policymaking aimed at addressing these inequalities not only requires immediate action to improve healthcare access but also involves long-term strategies to dismantle the systemic barriers that have historically marginalized these communities.
Addressing racial disparities in maternal mortality also necessitates a focus on cultural competency within the healthcare system. Ensuring that healthcare providers are trained to understand and respect the cultural differences and preferences of diverse patient populations can lead to more effective communication and better health outcomes. Additionally, community-led initiatives can help bridge gaps in understanding and trust between marginalized communities and healthcare systems. By involving community members in the development and implementation of maternal health programs, we can create a more equitable healthcare environment that not only seeks to reduce maternal mortality rates but also fosters a supportive atmosphere where all women feel valued and respected.
The Importance of Comprehensive Postpartum Care
Postpartum care should extend well beyond the critical first few weeks after childbirth. Recent studies reveal that nearly a third of maternal deaths occur between 42 days and one year after pregnancy. The conventional healthcare model often neglects this important period, leaving women vulnerable to complications that could be prevented with proper care. Many women experience a sudden drop in medical attention after the initial postpartum check-up, leaving them without the necessary support as they navigate recovery. Implementing a more robust and continuous model of postpartum care that emphasizes long-term health and wellbeing is essential for reducing maternal mortality rates.
Employers and policymakers also play a key role in ensuring better postpartum healthcare access. Increasing maternity leave can afford new mothers time to recover physically and mentally, encouraging them to attend regular follow-up appointments and seek help if complications arise. Improved education on postpartum wellness, including physical recovery and mental health screening, can empower women to prioritize their health after childbirth. In this way, comprehensive postpartum care must be viewed as an integral part of maternal health that warrants equal attention to the prenatal phase. By making these changes, we can help promote longer, healthier lives for mothers and ultimately reduce pregnancy-related deaths.
Addressing Pregnancy-Related Deaths: Key Strategies
To tackle the continuous rise in U.S. pregnancy-related deaths, a multi-faceted approach is necessary. First, the healthcare system needs to focus on enhancing access to comprehensive maternal health services, ensuring that women receive care before, during, and after pregnancy. This encompasses improving prenatal education, ensuring qualified healthcare providers are available, and expanding insurance coverage for maternity healthcare. Policymakers must also prioritize investment in maternal health infrastructure to create supportive healthcare environments that facilitate positive outcomes for all mothers.
Second, targeted interventions should be designed to address specific community needs, particularly in areas that show significant racial disparities in maternal health statistics. Implementing culturally competent care models, enhancing community health programs, and fostering partnerships with local organizations can help address these disparities. Finally, systemic changes that promote equitable healthcare access and outcomes are imperative. By focusing on quality care and personalized attention, we can help to reduce the incidence of preventable pregnancy-related deaths and ensure that all women can thrive during their reproductive years.
The Role of Public Health Infrastructure
A strong public health infrastructure is paramount in effectively addressing the challenges surrounding maternal mortality in the U.S. Research indicates that we cannot improve outcomes without consistent tracking and assessment of pregnancy-related deaths. The implementation of a nationwide system for monitoring maternal health statistics—such as the pregnancy checkbox on death certificates—is an essential step in gathering accurate data. Investing in these systems will aid policymakers in making informed decisions, allocating resources efficiently, and developing strategies that directly target the issues leading to preventable deaths.
Moreover, enhancing public health initiatives means increasing funding for maternal health research and advocacy efforts. As funding for these areas continues to decline, the risk of neglecting maternal health issues rises. By advocating for sustained investment in maternal health programs and public health campaigns, stakeholders can help raise awareness about the significance of maternal health and its implications. This support will not only contribute to reducing maternal mortality rates but also work towards fostering a healthier population long term. Having a strong foundation in public health can lead to substantial improvements, ultimately ensuring every mother has the opportunity to thrive.
Improving Access to Quality Prenatal Care
Improving access to quality prenatal care is crucial in addressing the preventable nature of most U.S. pregnancy-related deaths. Each year, many women enter pregnancy without adequate healthcare, which often exacerbates existing health issues and increases the risk of complications. Strategies to enhance access can include expanding telehealth services, providing transportation assistance, and increasing funding for community health centers that serve low-income populations. These initiatives can significantly mitigate barriers to care, making it easier for women to seek out and receive comprehensive prenatal services.
Moreover, healthcare professionals must be equipped with the necessary training to manage both straightforward and complex pregnancies. Continuous education programs and workshops should focus on the current maternal health landscape, the management of chronic diseases during pregnancy, and the importance of culturally competent care. By prioritizing comprehensive training alongside accessibility, healthcare providers can play an essential role in reducing the incidence of pregnancy-related deaths and creating a safer, more informed environment for women throughout their pregnancy journeys.
Innovative Solutions to Enhance Maternal Health
Innovative solutions are essential to enhancing maternal health outcomes in the U.S. and combating rising pregnancy-related mortality rates. One approach involves leveraging technology to support women’s health during pregnancy and postpartum periods. Mobile health apps that facilitate remote monitoring of vital signs, provide educational resources, and encourage regular check-ins with healthcare providers can empower women to take control of their health. Additionally, incorporating artificial intelligence and machine learning into health assessments can allow for personalized care plans that cater to an individual’s specific health risks.
Furthermore, developing community-based programs that integrate maternal health with mental health services can address the often-overlooked psychological issues associated with pregnancy and childbirth. Offering mental health screenings and therapies as part of standard prenatal and postnatal care can significantly contribute to overall maternal well-being. With innovative practices like these, it’s possible to create more resilient healthcare systems that prioritize women’s health throughout their reproductive lives, ultimately aiming to reduce the high rates of preventable pregnancy-related deaths in the U.S.
Advocacy for Maternal Health Policies
Advocacy plays a vital role in shaping maternal health policies and addressing the systemic issues contributing to the U.S. maternal mortality crisis. As the rates of pregnancy-related deaths continue to rise, engaging both women and healthcare providers in advocacy efforts can lead to powerful change. Grassroots movements, coupled with policy initiatives, help to raise awareness of the challenges faced by marginalized communities and can influence decision-makers to prioritize maternal health concerns.
To foster effective change, it is crucial to mobilize support from various stakeholders, including healthcare providers, policymakers, and community leaders. Collaborative efforts can create a unified front that presses for legislation aimed at improving maternal healthcare access, funding vital research, and dismantling systemic inequities. Advocacy for comprehensive maternal health policies not only aims to reduce pregnancy-related deaths but also works towards creating a healthcare landscape where all women have equal opportunities for healthy pregnancies and postpartum recovery.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the current state of U.S. maternal mortality rates?
The U.S. maternal mortality rate remains high, with recent data indicating 32.6 pregnancy-related deaths per 100,000 live births in 2022, an increase from 25.3 in 2018. This troubling trend highlights the urgent need for improvements in maternal health services and postpartum care.
What are the primary causes of pregnancy-related deaths in the U.S.?
Cardiovascular disease is the leading cause of pregnancy-related deaths in the U.S., accounting for just over 20% of cases. Other significant causes include hemorrhage and conditions like pre-eclampsia and cardiac arrest, emphasizing the importance of monitoring maternal health throughout pregnancy and the postpartum period.
How do racial disparities affect U.S. maternal mortality rates?
Racial disparities in U.S. maternal mortality are significant, with American Indian and Alaska Native women facing the highest rates at 106.3 deaths per 100,000 live births. Non-Hispanic Black women also experience high mortality rates, underscoring the need for targeted interventions to improve maternal health outcomes among these groups.
What changes are needed to reduce maternal mortality in the United States?
To lower U.S. maternal mortality rates, there must be increased investment in healthcare infrastructure, quality of care during pregnancy, and extended postpartum services. Addressing state-level disparities and creating equitable healthcare policies are essential components of this effort.
Why is postpartum care important in reducing maternal mortality?
Postpartum care is crucial because many maternal deaths occur between 42 days and one year after childbirth. Comprehensive postpartum support can help identify and manage health issues that arise after delivery, thus reducing the risk of late maternal deaths.
What role does cardiovascular disease play in U.S. maternal mortality statistics?
Cardiovascular disease now ranks as the leading cause of pregnancy-related deaths, reflecting a concerning trend as more women experience chronic conditions like hypertension at younger ages. This shift necessitates better screening and management of cardiovascular health in pregnant individuals.
How can states combat racial disparities in maternal health outcomes?
States can combat racial disparities in maternal health by implementing targeted policies that enhance access to quality care for marginalized communities, ensuring culturally competent care, and addressing systemic biases within healthcare systems.
What impact did the COVID-19 pandemic have on U.S. maternal mortality rates?
The COVID-19 pandemic likely contributed to a sharp increase in U.S. maternal mortality rates, particularly in 2021, by exacerbating existing healthcare disparities and limiting access to essential services for pregnant individuals.
What are late maternal deaths and why are they significant?
Late maternal deaths occur between 42 days and one year postpartum and are significant because they highlight the need for extended healthcare attention and resources during the postpartum period, as significant numbers of these deaths are preventable.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Rising Maternal Mortality | The U.S. has seen an increase in maternal mortality rates from 25.3 deaths per 100,000 live births in 2018 to 32.6 in 2022. |
| Preventable Deaths | Over 80% of pregnancy-related deaths are preventable in the U.S. |
| Racial Disparities | Significant disparities exist, with American Indian and Alaska Native women facing the highest mortality rate at 106.3 per 100,000 live births. |
| Impact of COVID-19 | The highest rate increase occurred in 2021, possibly reflecting pandemic-related impacts. |
| Leading Causes | Cardiovascular disease is now the leading cause of maternal death, comprising over 20% of fatalities. |
| Need for Innovation | Investments and innovative solutions are needed in prenatal and postpartum care to improve maternal health outcomes. |
Summary
U.S. maternal mortality remains a pressing public health issue, with the nation continuing to experience the highest rates among high-income countries. Efforts must focus on preventing the vast majority of preventable deaths, addressing systemic inequities, and improving healthcare access and quality, particularly in underserved communities. The rising trends in maternal mortality underscore the need for urgent action and commitment to enhancing both prenatal and postpartum care.