Stem cell therapy for cornea injuries represents a groundbreaking advancement in ophthalmologic treatment, offering new hope for patients previously considered untreatable. This innovative approach utilizes cultivated autologous limbal epithelial cells (CALEC) obtained from a healthy eye to regenerate and restore the corneal surface. The clinical trials have demonstrated remarkable efficacy, with over 90% of participants experiencing significant improvements in their vision after receiving these specialized stem cell grafts. As a unique cornea damage treatment, CALEC surgery stands to revolutionize corneal restoration practices by enabling recovery for individuals suffering from severe corneal injuries, such as chemical burns or infections. By harnessing the regenerative power of limbal epithelial cells, stem cell transplant eye procedures could redefine the future of vision rehabilitation.
The emergence of cellular therapy for corneal concerns has opened new avenues in eye care, involving the transplantation of healthy tissues derived from stem cells. Often referred to as corneal restoration techniques, these cutting-edge methods are designed to address complex cases of cornea damage that traditional surgical interventions might not resolve. By focusing on the repair of the cornea through innovative procedures like CALEC, patients with debilitating eye conditions are finding renewed hope for improved vision and quality of life. This type of treatment not only emphasizes the potential of regenerative medicine but also highlights the importance of limbal epithelial cells as crucial components in facilitating successful corneal recovery. As research progresses, these therapies may eventually become standard practices in ophthalmology.
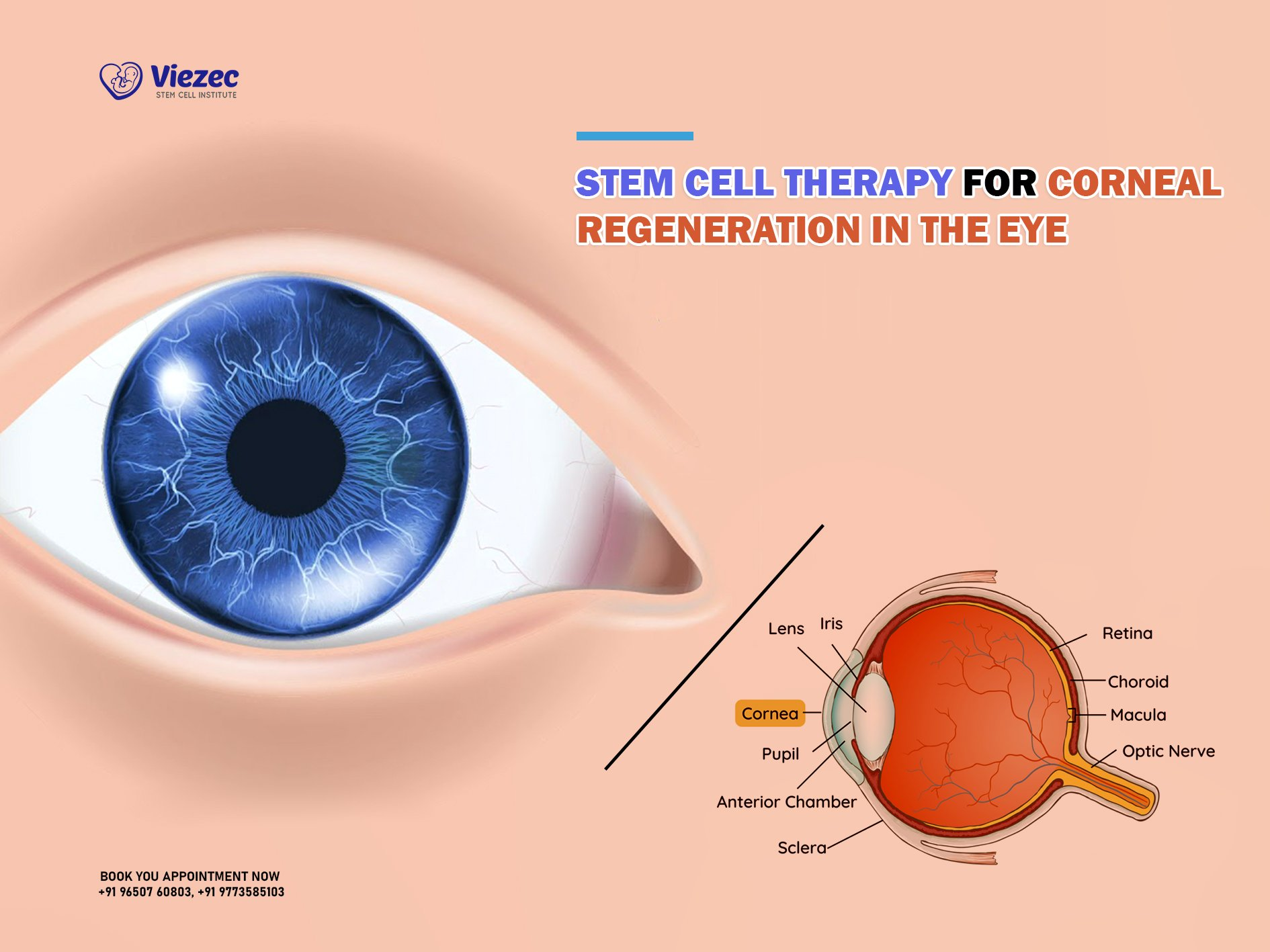
Understanding Corneal Damage and Its Impact on Vision
Corneal damage refers to any injury or illness that affects the cornea, the eye’s crucial outer layer. Factors contributing to this damage include chemical burns, infections, and injuries. Such damage can lead to significant visual impairment and persistent discomfort for those affected. The cornea provides most of the eye’s optical power, making it essential for clear vision. When the cornea suffers a significant injury, patients often find themselves struggling with light sensitivity, pain, and a severely diminished field of vision.
This burden isn’t just physical; it can deeply impact a person’s quality of life. Without proper treatment, conditions like limbal stem cell deficiency may arise, leading to chronic issues and potentially rendering corneal transplant procedures ineffective. The emerging solutions, including advanced therapies like CALEC surgery, are vital in addressing these debilitating conditions, paving the way for innovative approaches to cornea damage treatment.
The importance of addressing corneal damage goes beyond simple restoration of vision; it encompasses both psychological and social aspects. Patients often report feeling isolated or anxious due to their visual impairments. Thus, any breakthrough in corneal restoration is not only a medical triumph but also a significant step towards improving patients’ overall wellbeing. Collaborative efforts involving ophthalmologists, researchers, and institutions can lead to novel strategies that may dramatically reinstate quality of life for those suffering from corneal maladies.
Innovative Approaches to Corneal Restoration Using Stem Cells
Stem cell therapy, particularly cultivated autologous limbal epithelial cells (CALEC), represents a groundbreaking advance in corneal restoration. By utilizing healthy limbal epithelial cells harvested from a patient’s unaffected eye, this technique seeks to regenerate damaged corneal surfaces effectively. Clinical trials have demonstrated over 90% efficacy in restoring corneal integrity, enabling patients with previously irreparable damage to regain their vision. This innovative method counters traditional treatments, expanding the horizon for patients once deemed ineligible for standard corneal transplants.
CALEC surgery is a testament to the potential of cellular therapies in ophthalmology. The procedure involves a detailed process of stem cell extraction, growth in a lab environment, and eventual transplantation. Each step is meticulously designed to ensure the safety and efficacy of the graft, making it a pioneering approach in the field. As research continues, these stem cell transplant eye procedures could evolve into standard treatments for a range of corneal issues.
One of the remarkable features of CALEC technology is its personalized nature. Each patient’s treatment is tailored based on their unique cellular characteristics, improving outcomes markedly compared to one-size-fits-all methods. This innovation is needed considerably when we consider the limitations posed by traditional surgery, particularly in patients with significant limbal cell depletion. The CALEC technique not only fulfills the immediate need for visual rehabilitation but also encourages ongoing research into allogeneic sources of limbal stem cells, which could further broaden accessibility and treatment possibilities for those with corneal damage across both eyes.
The Future of Limbal Epithelial Cell Therapy for Vision Restoration
Looking ahead, the future of limbal epithelial cell therapy shines brightly with potential innovations on the horizon. The promising results from clinical trials encourage further research to expand the applicability of CALEC, particularly in cases involving both eyes. Scientists aspire to establish protocols for allogeneic stem cell sources, enabling treatment without localized limitations. This could significantly increase the pool of eligible patients and facilitate access to cutting-edge therapies for cornea damage treatment.
With support from the National Eye Institute and collaborations with numerous research institutions, the hope is for CALEC surgery to transition into a mainstream procedure. The progressive nature of this therapy indicates a shifting paradigm in how corneal injuries are treated, signifying a move away from conventional transplants towards innovative regenerative treatments guided by cellular biology.
Additionally, ongoing clinical trials are crucial for corroborating the safety and effectiveness of CALEC therapy, ultimately aiming for FDA approval. Enhanced long-term data collection will provide insights into the durability of visual improvement and graft survival rates, essential aspects for both practitioners and patients. As interest in stem cell therapies grows within the ophthalmological community, there is a burgeoning belief that breakthroughs in corneal restoration using limbal epithelial cells will herald a new epoch in eye care, fostering hope for countless individuals assailed by corneal damage.
Regulatory Considerations and Advancements in Stem Cell Research
As with any innovative medical procedure, regulatory considerations play a pivotal role in the advancement and implementation of stem cell-based therapies like CALEC. The trajectory from a successful clinical trial to widespread clinical application hinges upon rigorous evaluation from authorities such as the FDA. This regulatory scrutiny ensures that treatments not only deliver effective medical outcomes but are also safe for patient populations. As researchers gather more data supporting the efficacy and safety profiles of CALEC, it becomes imperative to navigate this regulatory landscape carefully to promote timely patient access to life-changing therapies.
The clinical journey of CALEC has already witnessed significant milestones since its inception, marking it as a trailblazer for research into ocular stem cell therapies. Collaborative efforts between scientists, regulatory bodies, and educational institutions are vital for creating frameworks that facilitate drug development while ensuring ethical compliance. As the body of research expands around stem cell applications in ophthalmology, it will be essential to maintain transparent communication with the public and healthcare professionals regarding the processes, benefits, and potential risks.
Advancements in stem cell research are set to redefine ophthalmology, particularly in addressing corneal injuries which were once categorized as untreatable. The ongoing dialogue about the ethical implications of stem cell use and potential commercial viability will shape future research directions. Encouragingly, the success of early-stage trials, like those surrounding CALEC, can serve as a foundation for subsequent exploration into broader applications of stem cell technologies, including alternative cell types or combinations that may optimize healing and reconstruction of ocular tissues.
Patient Perspectives on the Efficacy of CALEC Surgery
Patient feedback is invaluable as clinical trials evolve into established treatments. The experiences of individuals who have undergone CALEC surgery are critical to understanding the practical implications of stem cell therapies for cornea damage. Many participants in the clinical trials have reported significant improvements in visual acuity and a decrease in discomfort after undergoing the procedure. Personal testimonials reveal the profound impact that restoring vision can have on day-to-day activities, emotional well-being, and overall quality of life.
These patient narratives highlight the human aspect behind clinical research, emphasizing the importance of continual communication between healthcare providers and patients throughout the treatment process. The perspectives secured from those who experienced CALEC provide vital insights that can guide refinements to the procedure, ensuring that it aligns well with patient needs and addresses concerns effectively.
However, while many patients experience positive outcomes, it is important to acknowledge those who may have had less favorable results. Documenting every aspect of patient experience — successes and setbacks — enables researchers to enhance protocol efficacy continually. It can also inform newly diagnosed patients about realistic expectations and the overall journey they may experience. As CALEC surgery progresses toward mainstream acceptance, gathering and analyzing patient perspectives will play an essential role in optimizing treatment approaches, ensuring they remain patient-centered and focused on improving visual health.
The Role of Research Collaborations in Advancing Stem Cell Therapies
Research collaborations between institutions and experts are instrumental in accelerating the development of innovative therapies like CALEC for cornea restoration. The joint efforts of notable organizations, including Mass Eye and Ear, Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, and Boston Children’s Hospital, underscore the multidisciplinary approach required to make significant advancements in the field of ocular medicine. Through collaborative research, diverse expertise converges, leading to enriched innovation that can drive scientific discovery and clinical application efficiently.
These partnerships not only enhance the technological and scientific tools available but also open pathways for shared funding, knowledge exchange, and broader clinical trials, increasing the robustness of research outcomes. A united front among medical fields can respond effectively to complex challenges, ensuring that cutting-edge treatments remain data-driven and informed by the latest findings in cell biology and regenerative medicine.
Moreover, strong research networks foster the development of protocols that encourage ethical considerations, patient safety, and compliance with regulatory standards. As the CALEC procedure evolves, the continuity of research collaboration ensures that there is a comprehensive understanding of the treatment’s effects, side effects, and overall patient experience. Such harmonized efforts can lead to expedited pathways for research translation into clinical practice, ultimately resulting in more efficient delivery of innovative therapies to those in need of corneal restoration.
The Importance of Continued Research in Ocular Stem Cell Therapy
The realm of ocular stem cell therapy requires persistent research to unlock its full potential. While CALEC has shown remarkable promise in addressing cornea damage, ongoing studies are essential for refining techniques, expanding applications, and verifying long-term outcomes. Continuous investigation may lead to innovations that enhance the safety and effectiveness of stem cell therapies, creating broader solutions for various eye conditions. By supporting large-scale, multi-center trials, researchers can obtain robust data that could catalyze shifts in treatment paradigms across the field.
The data garnered from extensive trials will also support the establishment of evidence-based guidelines for implementing these therapies in clinical practice. Future studies should focus on diverse populations to truly understand the variability in results and make necessary adjustments to protocols. As our comprehension deepens, the march towards FDA approval and general clinical use of CALEC will become more achievable.
Research funding from entities such as the National Eye Institute is crucial for fostering this exploration and promoting interdisciplinary collaboration among institutions. By prioritizing ocular stem cell research, we can ensure that the upcoming generation of practitioners is equipped with the latest knowledge and tools to tackle corneal impairments effectively. Engaging in translational research that bridges laboratory discoveries to clinical applications will significantly impact not only patient treatment but the overall model of care within ophthalmology.
Ethical Considerations in Stem Cell Therapies for Ophthalmology
As with any groundbreaking medical innovation, the emergence of stem cell therapies in ophthalmology brings forth important ethical considerations. The appeal of stem cell treatments lies in their regenerative potential; however, managing the ethical dilemmas around their use is imperative. Informed consent, patient autonomy, and the origins of stem cells are central concerns that practitioners and researchers must navigate delicately. Ensuring that patients fully understand the risks, benefits, and uncertainties of the procedures is crucial for fostering trust and safety in emerging treatment options like CALEC surgery.
Ethical guidelines must evolve in tandem with advances in the field to safeguard both patients and healthcare providers. In this context, establishing a robust ethical framework will not only enhance the credibility of new treatments but also help foster open dialogue regarding both the potential and pitfalls associated with stem cell research. It is important that the development of these therapies occurs transparently, with ongoing discussions surrounding ethical practices and patient rights.
Moreover, the relationship between innovation and ethics must be viewed through a lens of inclusivity and accessibility. As treatments like CALEC become available, ensuring equitable access across diverse patient populations becomes a critical ethical imperative. Discussions around funding, insurance coverage, and the socioeconomic implications of such therapies must take place to ensure that all patients have an opportunity for restoration and improved quality of life, regardless of background or circumstances. Embracing a comprehensive ethical approach will foster greater public trust and acceptance of emerging stem cell therapies in the field of ophthalmology.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is stem cell therapy for cornea and how does it work?
Stem cell therapy for the cornea involves using cultivated autologous limbal epithelial cells (CALEC), which are stem cells taken from a healthy eye to treat corneal damage. The process includes a biopsy of the healthy eye to harvest these cells, expanding them in culture to create a graft, and then transplanting this graft into the damaged eye. This therapy aims to restore the cornea’s surface and function, particularly for patients with injuries like chemical burns or infections.
What is CALEC surgery and who can benefit from it?
CALEC surgery is a specific type of stem cell therapy for cornea damage; it involves transplanting cultivated autologous limbal epithelial cells into a damaged eye. This surgery can benefit patients suffering from limbal stem cell deficiency due to conditions that do not allow for traditional corneal transplants. Candidates typically include those with permanent corneal damage from injuries that deplete limbal epithelial cells.
What are limbal epithelial cells and their role in corneal restoration?
Limbal epithelial cells are specialized stem cells located at the limbus, the border of the cornea. They play a critical role in maintaining the cornea’s surface integrity and transparency. In cases of corneal damage or diseases leading to limbal stem cell deficiency, these cells can be depleted, necessitating treatments like stem cell therapy for cornea restoration.
How effective is stem cell therapy for cornea compared to traditional treatments?
Stem cell therapy for cornea, specifically CALEC surgery, has shown more than 90% effectiveness in restoring corneal surfaces in clinical trials. This success rate is significant compared to traditional treatments, which may not always reverse severe corneal damage or are limited by the availability of donor tissue for transplants.
What are the risks associated with stem cell transplant for the eye?
While stem cell therapy for the cornea, particularly CALEC surgery, has demonstrated a high safety profile in trials, risks still exist. These can include mild adverse events like infections or complications related to the surgical procedure. Most adverse events observed were minor and resolved without long-term issues.
Is stem cell therapy for cornea currently available in the U.S.?
As of now, stem cell therapy for the cornea, such as CALEC surgery, remains experimental and is not yet available in U.S. hospitals. Ongoing clinical trials are necessary to further evaluate its effectiveness and safety before seeking federal approval for broader use.
What future developments are expected in stem cell therapy for cornea?
Future developments in stem cell therapy for cornea may include establishing an allogeneic manufacturing process, allowing for the use of limbal stem cells from cadaveric eye donors. This could expand treatment options for patients with bilateral corneal damage and enhance the availability and accessibility of CALEC treatments.
How does the stem cell therapy for cornea improve visual acuity?
In clinical trials, patients undergoing stem cell therapy for cornea reported varying improvements in visual acuity. As the therapy restores the cornea’s surface, it can alleviate pain and enhance clarity of vision, which is particularly beneficial for individuals with significant corneal injuries that lead to visual impairment.
What should patients expect during recovery from CALEC surgery?
Recovery from CALEC surgery involves monitoring for any signs of infection and attending follow-up appointments. Patients may experience gradual improvements in their vision and discomfort. Most reported side effects were manageable and did not hinder recovery, leading to significant enhancements in their quality of life.
What is the role of the FDA in the development of stem cell therapies for the eye?
The FDA plays a crucial role in the development and approval of stem cell therapies for the eye, including the CALEC procedure. Approval ensures that treatments meet safety and efficacy standards, facilitating access to innovative therapies for patients with corneal damage once comprehensive trials are completed.
| Key Points |
|---|
| Ula Jurkunas performs the first CALEC surgery at Mass Eye and Ear as part of a groundbreaking trial. |
| Stem cell therapy for corneal injuries, known as CALEC, involves transplanting cultured limbal epithelial cells from a healthy eye. |
| Clinical trials demonstrated that the CALEC method successfully restored corneal surfaces in 14 patients over 18 months. |
| The trial showed CALEC had a success rate of over 90%, significantly improving outcomes for patients with previously untreatable corneal damage. |
| The study indicates that complete cornea restoration was achieved in 50% of patients by three months, increasing to 79% and 77% at 12 and 18 months respectively. |
| Future plans include researching allogeneic manufacturing processes to treat patients with damage to both eyes. |
| The trial is the first of its kind in the U.S. to receive funding from the National Eye Institute and aims for FDA approval in the future. |
Summary
Stem cell therapy for cornea offers a promising new approach in the treatment of corneal injuries previously deemed untreatable. The recent clinical trial conducted at Mass Eye and Ear has illustrated the potential of CALEC (cultivated autologous limbal epithelial cells) to safely restore corneal surfaces in patients by utilizing stem cells harvested from their healthy eyes. With over 90% effectiveness reported in restoring vision and alleviating symptoms, this innovative procedure represents significant hope for individuals suffering from severe corneal damage. As further studies move forward, the path towards broader application and FDA approval appears bright, setting the stage for expanded accessibility to this transformative treatment.