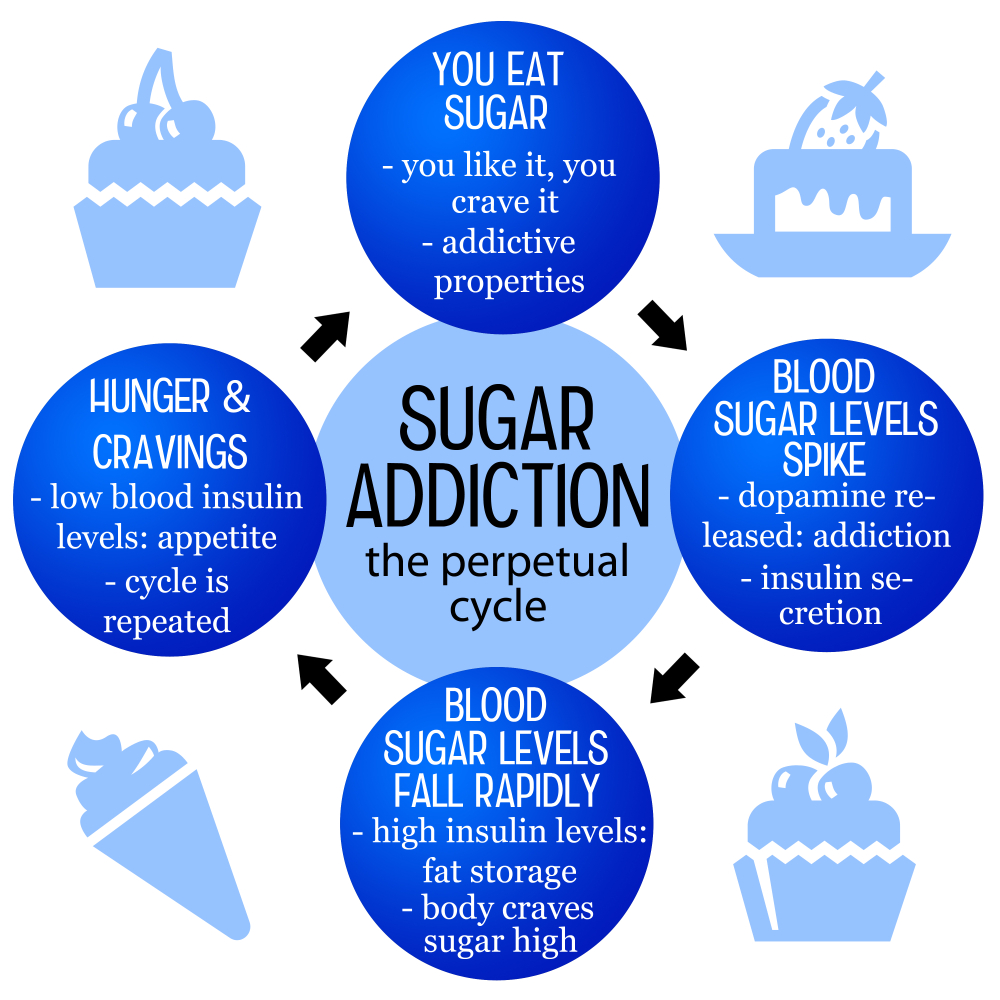
Is sugar addictive? This question has sparked heated debates among nutrition experts and the general public alike. While substances like alcohol and nicotine are clinically recognized as addictive due to their severe impairments on health and behavior, sugar’s role in our diets prompts a complex discussion. Many people experience intense sugar cravings that lead to compulsive food consumption, especially with the increase of added sugar in ultra-processed foods. These cravings can create withdrawal-like symptoms, such as headaches and anxiety, when one tries to cut down on added sugar consumption. Understanding the health risks of sugar and finding a balance might help mitigate the effects of food addiction and promote a healthier relationship with our diets.
When we explore the concept of sugar dependency further, we can also refer to it as a form of food addiction—a condition where individuals find it challenging to control their intake of certain types of food, particularly those high in sweeteners. This reliance on sugary foods might lead to what some describe as sugar withdrawal symptoms, including irritability and discomfort when access to sugar is restricted. The omnipresence of added sugar in our diets raises the question of how society views this substance compared to other addictive elements. As more people strive to reduce their consumption of sugary products, understanding the psychological implications becomes crucial. Ultimately, gleaning insights about the nuances of sugar cravings and their potential health risks can empower individuals to make more informed nutritional choices.
Understanding Sugar Cravings and Their Effects
Sugar cravings are a common experience, often leading individuals to seek out sweet foods for immediate pleasure and satisfaction. Nutrition experts note that these cravings can be exacerbated by the consumption of ultra-processed foods, which not only contain high levels of added sugar but also unhealthy fats and sodium. These combinations make the foods incredibly palatable, prompting frequent consumption and ultimately reinforcing the cycle of craving. Over time, this can lead to a kind of food addiction, where the brain’s reward system becomes overly reliant on sugar-rich foods in the same way it might on more traditionally addictive substances.
When an individual reduces their sugar intake, they may experience withdrawal-like symptoms similar to those linked to substance use disorders. Headaches, irritability, and anxiety can emerge as the body adjusts to lower sugar levels, highlighting the powerful impact sugar has on our brain and mood. This phenomenon underscores the importance of recognizing that while sugar is not classified as a traditional addictive substance, its biological effects and impact on eating habits suggest a complex relationship that warrants further understanding.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is sugar addictive in the same way that drugs like nicotine or alcohol are?
While sugar can lead to cravings and compulsive eating behaviors, it is not classified as an addictive substance like alcohol or nicotine. Sugar does stimulate pleasure centers in the brain, which may make it addictive-like, but its effects and withdrawal symptoms are generally less severe.
What are sugar cravings and how are they related to sugar addiction?
Sugar cravings occur when the body seeks out sugar for instant energy and pleasure. Although they may resemble addiction symptoms, these cravings stem from the body’s reaction to processed foods high in added sugars, which can lead to habitual consumption but don’t meet the strict criteria for addiction.
What health risks are associated with high added sugar consumption?
High added sugar consumption is linked to various health risks such as obesity, type 2 diabetes, heart disease, and increased triglyceride levels. Limiting added sugar intake can help mitigate these risks and promote overall health.
Are sugar withdrawal symptoms common when reducing sugar intake?
Yes, some individuals may experience withdrawal-like symptoms when reducing sugar intake, including headaches, dizziness, and anxiety. These symptoms arise from the sudden decrease in consumptive habits associated with high-sugar foods.
How can someone manage sugar cravings to avoid food addiction?
To manage sugar cravings, it’s important to gradually reduce the intake of added sugars rather than cutting them out completely. Focus on a balanced diet rich in whole foods like fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, which provide natural sugars in moderation without the health risks of processed snacks.
What are some effective strategies for reducing added sugar consumption?
To reduce added sugar consumption, read food labels to identify hidden sugars, gradually lessen sugary snacks and beverages from your diet, and replace them with healthier options like fruits and yogurt. Making small adjustments can lead to lasting changes.
Can sugar in moderation be part of a healthy diet?
Yes, sugar in moderation can enhance flavor and enjoyment in food. The key is to limit added sugars to recommended levels, such as 9 teaspoons per day for men and 6 for women, to stay within a healthy dietary range.
| Key Point | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Cravings and Consumption | Sugar can increase cravings and compulsive eating behaviors, leading to habitual consumption. |
| Addiction Classification | Unlike alcohol and nicotine, sugar is not classified as an addictive substance despite having addictive qualities. |
| Effects of Withdrawal | Stopping sugar abruptly can cause withdrawal-like symptoms, although they are less severe compared to drugs. |
| Natural Presence in Foods | Sugar is naturally found in many healthy foods like fruits and dairy, complicating its classification as a drug. |
| Recommended Sugar Intake | The American Heart Association recommends limiting added sugar intake to 9 teaspoons for men, 6 for women, and less for children. |
| Gradual Reduction | Going ‘cold turkey’ on sugar can backfire; it’s better to reduce intake gradually. |
| Moderation is Key | In moderation, sugar can enhance flavor and enjoyment in food, highlighting the importance of balance. |
Summary
Is sugar addictive? This question has sparked considerable debate among nutrition experts. While sugar can trigger cravings and compulsive eating behaviors similar to addictive substances, it is not classified as an addictive agent like alcohol or nicotine. The body requires certain sugars found in nutrient-rich foods, making total elimination impractical. Current recommendations suggest limiting added sugar intake to promote better health. Understanding the role of sugar in our diet, and recognizing the difference between habitual consumption and addiction, is crucial for maintaining a balanced relationship with sweetness.